이번 글에서는 C#을 이용하여 dll을 만들고 WPF 프로그램에서 사용해보도록 하겠습니다. dll이 무엇인지는 쉽게 나오니 바로 만들어 보도록 하겠습니다.
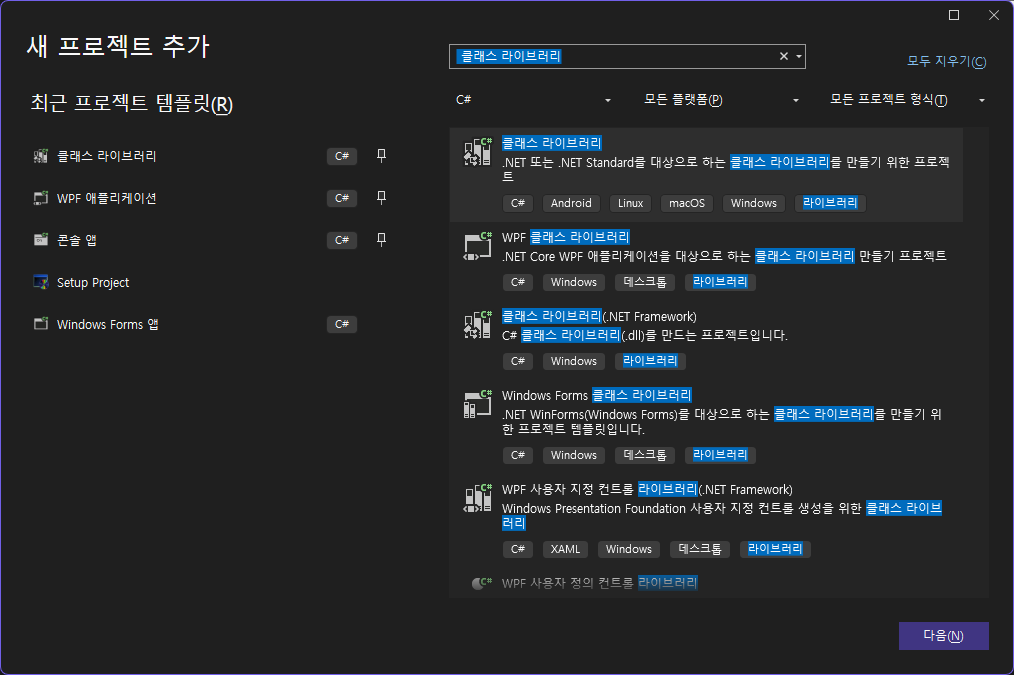
C#을 사용하여 dll을 만들 땐 클래스 라이브러리 프로젝트를 선택하면 됩니다.
라이브러리 이름은 MathLibrary으로 하고 아래와 같이 Calculator.cs를 하나 만들어 줍니다. 그리고 아래와 같이 코딩해줍니다.
namespace MathLibrary
{
public class Calculator
{
public int Add(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
}
}
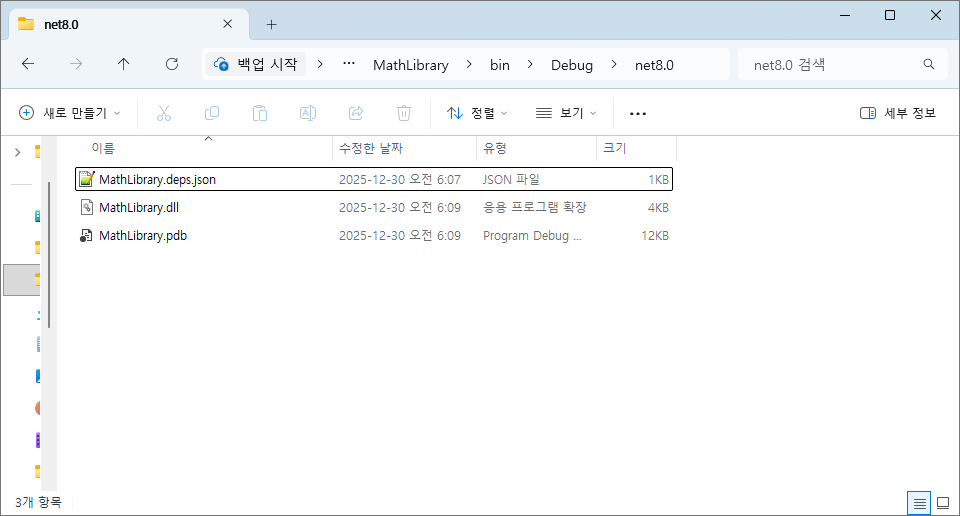
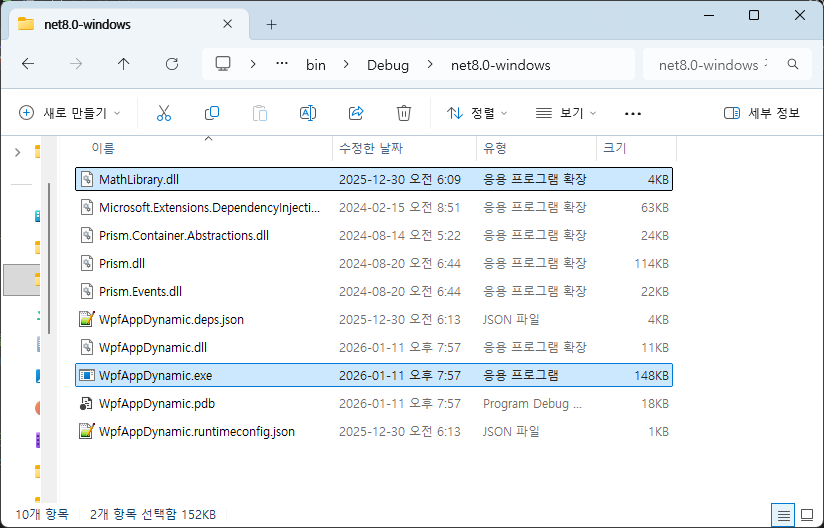
위 함수는 더하기 함수 입니다. 이 상태로 빌드하면 경로에 dll이 생성 된 것을 볼 수 있습니다.
이제 라이브러리에 넣은 Add라는 함수를 WPF에서 정적, 동적으로 불러와 함수를 호출해 보겠습니다.
정적 참조
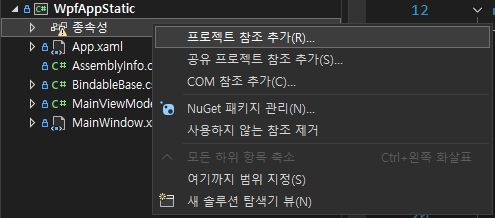
정적으로 참조하는 방법은 어렵지 않습니다. WPF 프로젝트를 하나 생성한 뒤에 프로젝트의 종속성을 우클릭해서 프로젝트 참조 추가를 클릭해줍니다.
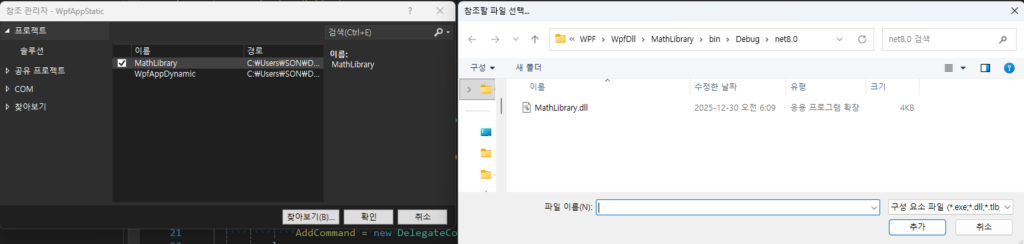
그리고 아까 만들어 놓은 dll을 참조합니다.
그 다음 MainWindow.xaml과 MainViewModel.cs에 아래와 같이 만들어 줍니다.
<Window x:Class="WpfAppStatic.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:d="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/blend/2008"
xmlns:mc="http://schemas.openxmlformats.org/markup-compatibility/2006"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfAppStatic"
mc:Ignorable="d"
Title="MainWindow"
Height="450"
Width="800">
<StackPanel>
<Button Content="Add"
Command="{Binding AddCommand}"/>
</StackPanel>
</Window>
using MathLibrary; // MathLibrary
namespace WpfAppStatic
{
public class MainViewModel : BindableBase
{
public DelegateCommand AddCommand { get; private set; }
delegate int AddDelegate(int a, int b);
public MainViewModel()
{
AddCommand = new DelegateCommand(OnAdd);
}
private void OnAdd()
{
Calculator c = new Calculator();
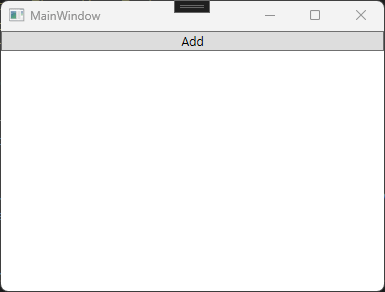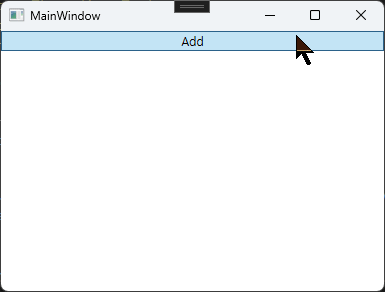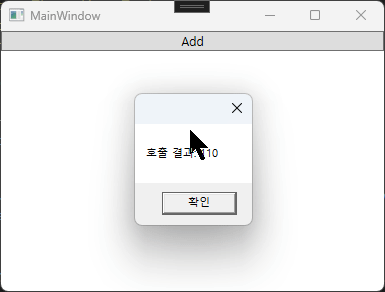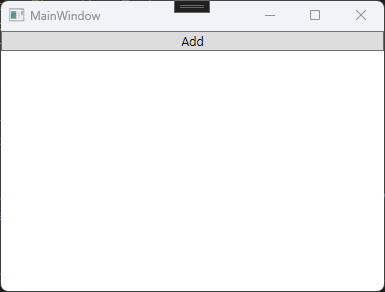
int result = c.Add(50, 60);
MessageBox.Show($"호출 결과: {result}");
}
}
}
using MathLibrary하여, Calculator 객체를 생성한뒤 Add 함수를 사용할 수 있습니다. 실행하면 아래와 같이 동작합니다.
동적 로딩
동적 로딩은 말 그대로 dll파일을 동적으로 로딩하는 방식입니다. 아까 만들어둔 MathLibrary.dll 파일을 exe 파일 위치랑 같이 위치시켜 줍니다.
동적 로딩으로 함수를 호출하는 방식은 총 3개 입니다
- dynamic 방식 : 컴파일러가 형 검사를 유예하며 런타임에 메서드를 찾아 실행합니다.
- Invoke 방식 : 메서드 정보를 통해 파라미터를 배열 형태로 전달하여 호출합니다.
- Delegate 방식 : 메서드 정보를 특정 대리자 형식으로 변환하여 연결합니다. 이후 호출부터는 리플렉션 비용 없이 직접 호출과 유사한 속도로 작동합니다.
private void OnAdd()
{
// DLL 파일을 런타임에 메모리로 로드합니다.
Assembly assembly = Assembly.LoadFrom("MathLibrary.dll");
if (assembly == null)
return;
// DLL 내부의 특정 클래스(네임스페이스 포함) 정보를 가져옵니다.
Type? type = assembly.GetType("MathLibrary.Calculator");
if (type == null)
return;
// 찾은 클래스 타입을 바탕으로 실제 객체(인스턴스)를 생성합니다.
dynamic? instance = Activator.CreateInstance(type);
if (instance == null)
return;
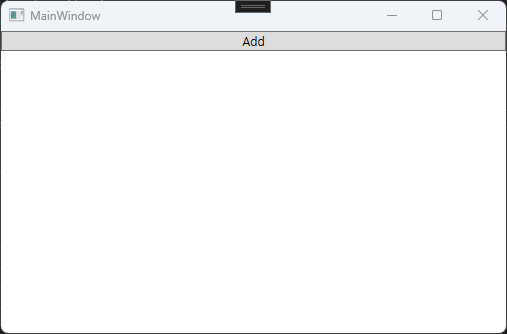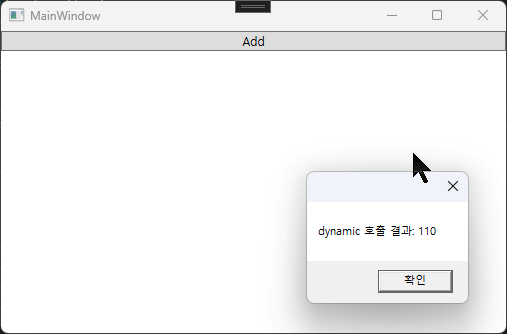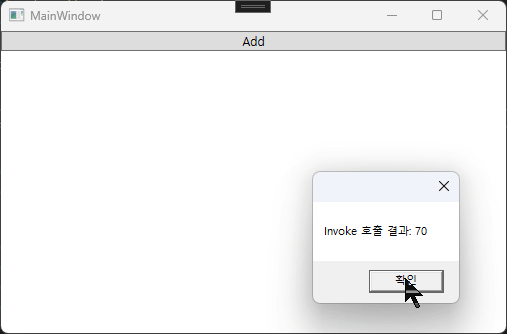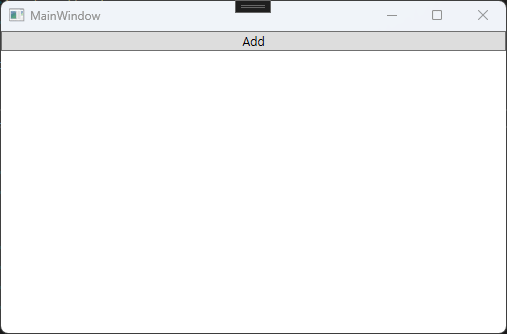
// 1. dynamic 방식: 컴파일러가 형 검사를 유예하며, 런타임에 메서드를 찾아 실행합니다.
int result = instance.Add(50, 60);
MessageBox.Show($"dynamic 호출 결과: {result}");
// 리플렉션을 통해 "Add"라는 이름의 메서드 메타데이터를 추출합니다.
MethodInfo? method = type.GetMethod("Add");
if (method == null)
return;
// 2. Invoke 방식: 메서드 정보를 통해 파라미터를 배열 형태로 전달하여 호출합니다.
object[] parameters = { 30, 40 };
result = (int)method.Invoke(instance, parameters);
MessageBox.Show($"Invoke 호출 결과: {result}");
// 3. Delegate 방식: 메서드 정보를 특정 대리자(AddDelegate) 형식으로 변환하여 연결합니다.
// 이후 호출부터는 리플렉션 비용 없이 직접 호출과 유사한 속도로 작동합니다.
AddDelegate addFunc = (AddDelegate)Delegate.CreateDelegate(typeof(AddDelegate), instance, method);
if (addFunc == null)
return;
result = addFunc(50, 60);
MessageBox.Show($"대리자 호출 결과: {result}");
}
실행하여 확인합니다.
github : https://github.com/3001ssw/c_sharp/tree/main/WPF/WpfDll
![[C#] dll 만들어 사용하기](https://3001ssw.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/12/blog_main_banner3.png)