C#의 checked와 unchecked 문은 오버플로우 검사 여부를 제어하는 키워드입니다. 정수 계산에서 값이 자료형의 범위를 벗어날 때 예외를 던질지, 그냥 넘어갈 지를 결정합니다. 정수 계산에서 오버플로우가 발생하면 System.OverflowException이 throw됩니다. 기본 명령문은 unchecked입니다. 즉 기본적으로 체크하지 않는 상태이며 checked 블록을 통해 오버플로우 검사를 켤 수 있습니다.
예제
uint a = uint.MaxValue;
unchecked
{
Console.WriteLine(a + 3); // output: 2
}
try
{
checked
{
Console.WriteLine(a + 3);
}
}
catch (OverflowException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message); // output: Arithmetic operation resulted in an overflow.
}
a에 uint의 최대값을 할당 했고, unchecked에서 +3을 하여 2가 출력됩니다. 하지만 checked 블록에서 +3을 하면 OverflowException가 발생합니다.
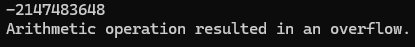
double a = double.MaxValue;
int b = unchecked((int)a);
Console.WriteLine(b); // output: -2147483648
try
{
b = checked((int)a);
}
catch (OverflowException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message); // output: Arithmetic operation resulted in an overflow.
}
checked((int)a) 와 같이 타입 변환에서도 checked 또는 unchecked 연산자를 붙일 수 있습니다.
int Multiply(int a, int b) => a * b;
int factor = 2;
try
{
checked
{
Console.WriteLine(Multiply(factor, int.MaxValue)); // output: -2, 함수 내 오버플로우 검사 X
}
}
catch (OverflowException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message);
}
try
{
checked
{
Console.WriteLine(Multiply(factor, factor * int.MaxValue));
}
}
catch (OverflowException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message); // output: Arithmetic operation resulted in an overflow.
}
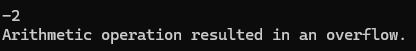
첫 번째 Multiply 함수 호출은 예외가 발생하지 않습니다. 왜냐하면 Multiply 함수 내부의 연산이 checked 블록 내부에 ‘텍스트’로 포함된 연산이 아니기 때문입니다.
반면에 두 번째 호출에서는 factor * int.MaxValue라는 연산이 checked 블록 내부에 직접 ‘텍스트’로 포함되므로 예외가 발생합니다.
기본 동작 및 주의사항
- 기본적으로 정수형 산술 연산 및 변환은 unchecked 컨텍스트에서 실행됩니다.
- 다만 상수 표현식(constant expression) 은 기본적으로 checked 컨텍스트에서 평가되며, 범위를 넘으면 컴파일 시간 오류가 발생합니다.
- decimal, float, double 등의 타입에서는 wrap-around 동작이 “의미 있다”고 보지 않기 때문에 unchecked 컨텍스트에서도 오버플로우일 때 예외가 발생할 수도 있습니다.
- 어떤 연산이 “검사 대상”이 되는지는 연산자 종류(+,-,*,/, ++, — 등)와 피연산자 타입에 따라 다릅니다.
오버플로우가 설계 상 절대로 발생해서는 안 되는 경우, 예를 들어 금융, 중요 데이터 처리에 checked 블록을 사용해서 문제를 조기에 발견하도록 하는 것이 좋습니다.
github : https://github.com/3001ssw/c_sharp/tree/main/basic/check_unchecked
![[C#] checked, unchecked](https://3001ssw.com/wp-content/uploads/2026/01/blog_main_banner4.png)